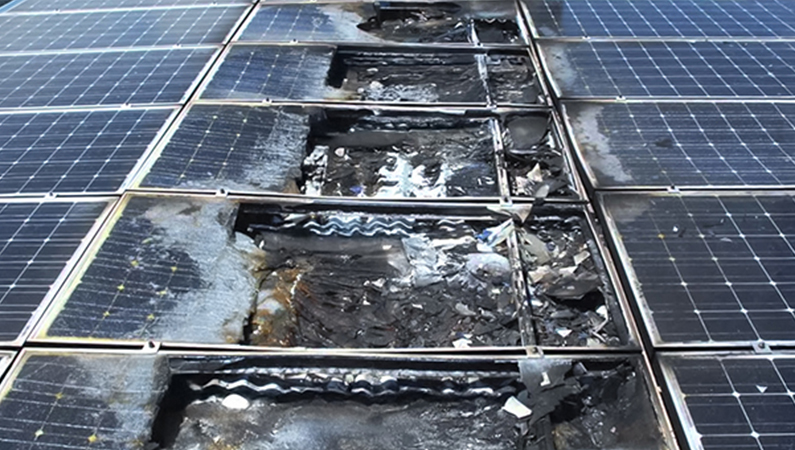
Solar Power Plants (SPP) are one of the main sources of sustainable energy production. However, early fault detection is critical for these systems to operate at maximum efficiency. At this point, thanks to the environmental sensor solutions developed by SEVEN, fault detection with sensor data becomes possible.
In this article, we will examine in detail the types of sensors used in SPP sites and how fault detection and preventive maintenance processes can be optimized with the data provided by these sensors.
Seven Sensors Used in Solar Power Plant (SPP) Sites
1. Irradiance Sensor and Thermopile Pyranometer

According to section “8.1 Sensor types” of the IEC 61724-1:2021 standard, pyranometers and irradiance sensors (reference cells) are used to measure total broadband hemispheric solar radiation, regardless of spectral or angular distribution. These sensors are used in solar power plants to monitor and evaluate system performance by measuring the amount of irradiance received. This data is compared with the energy produced to evaluate the performance. If the amount of light the panel should receive is compared with the energy produced, efficiency loss and panel failures are detected. For example, low production values can be an indicator of ghosting, contamination or cell failure.
2. Module and Ambient Temperature Sensor

According to IEC 61724-1:2021, module and ambient temperature sensors are used to evaluate the performance of photovoltaic systems in relation to environmental conditions. Module temperature is a critical parameter in performance ratio (PR) calculations as it directly affects production efficiency, while ambient temperature provides a reference to analyze the thermal behavior of the system. Panel temperature sensors monitor module temperature and detect problems such as overheating. Ambient temperature sensors evaluate environmental conditions and analyze the factors affecting the efficiency of the panels. With this sensor data, the user is warned about the difference between panel and ambient temperature at SPP sites, the effect of wind speed and cooling, excessive temperatures, thermal failures or connection problems.
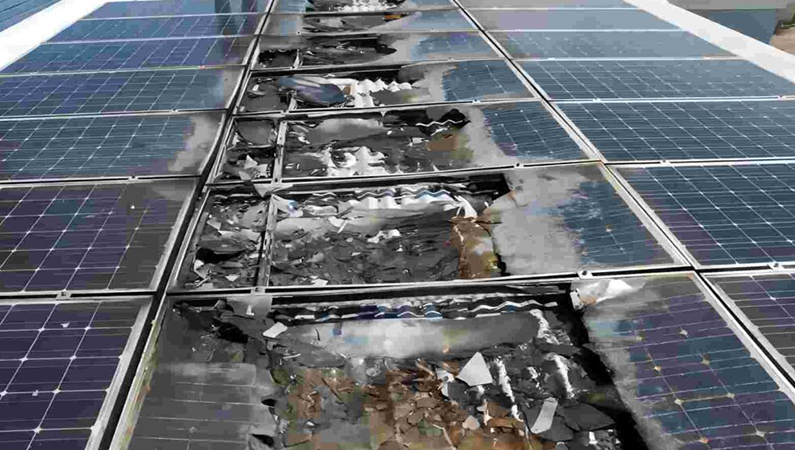

Damage to Solar Modules After High Temperature
3. Relative Humidity Sensor
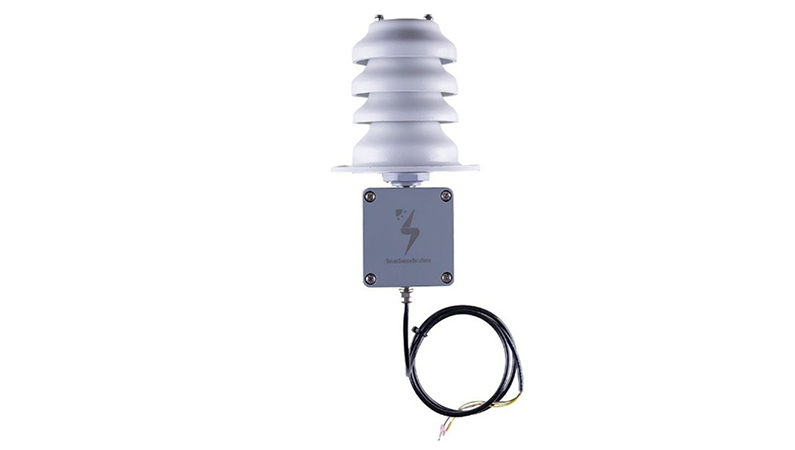

According to IEC 61724-1:2021 standard, section “9.7 Humidity”, relative humidity measurements can be used to estimate changes in the incident spectrum that can affect the PV module power output as well as the irradiance sensor readings. Using humidity data in combination with temperature data, wet times due to condensation can also be calculated. (Alternatively, surface condensation sensors can be used to collect this data directly.) Deviations are detected with the associated humidity data and field protective measures are taken, such as preventing misleading data or informing maintenance teams.
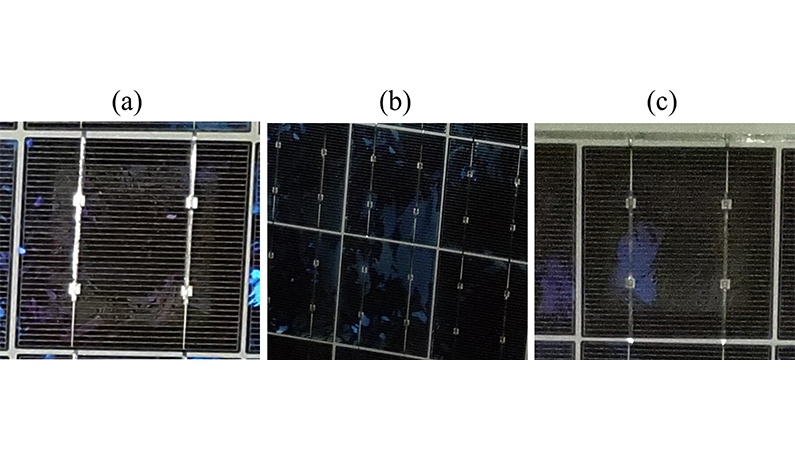
(a) Delamination around solar cell edges, (b) discolouration of encapsulants, and (c) oxidation of metal grids as a result of moisture ingress
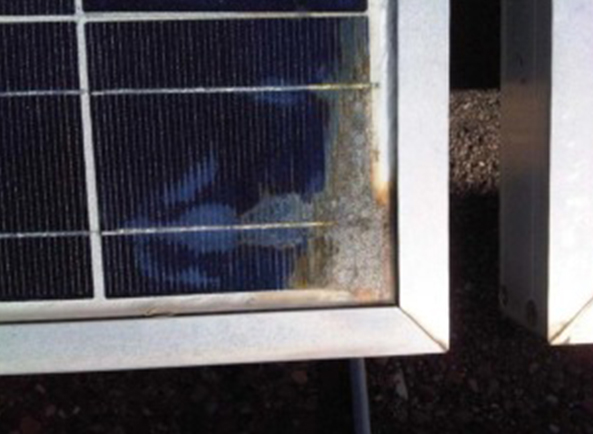

A typical moisture ingressed PV module showing signs of corroded metal grids, delamination and discolouration of encapsulants
4. Rain Gauge Sensor

According to IEC 61724-1:2021 standard, section “9.5 Rainfall”, Rain Gauge can be used to estimate the cleanliness of modules. If the contamination rate is also measured, these data are complementary. So with rain sensors, it evaluates the natural cleaning processes by detecting the amount of rain. In addition, these sensors can instantly detect the onset and intensity of rainfall, providing timely information to maintenance and operations teams about slipperiness in the field, wet equipment or delayed scheduled panel cleaning.
5. Wind Speed and Direction Sensor

According to IEC 61724-1:2021 standard “9.3 Wind speed and direction” Wind speed and wind direction are used to estimate module temperatures. It can also be used to document warranty claims for wind-related damage. Wind can indirectly change system efficiency by affecting module temperature; it is also a critical parameter for structural safety. Wind sensors assess the risk of high wind speeds damaging panels. Excessive wind can cause damage to load-bearing systems.

Damage to Solar Modules After High Wind
6. Soiling Sensor
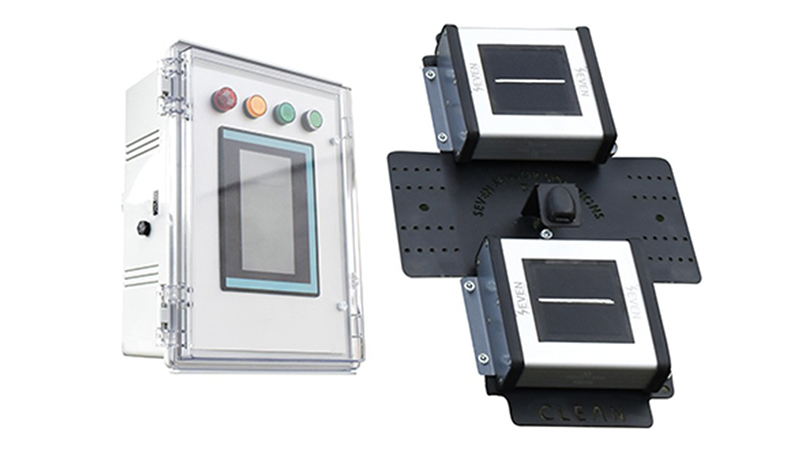

According to IEC 61724-1:2021, soiling sensors are used to monitor radiation losses caused by dirt and dust accumulated on the surface of PV panels. Since contamination reduces panel efficiency, these sensors help optimize cleaning timing and provide accurate analysis of performance degradation. Dust and dirt on the panel surface cause efficiency loss and hot spots. With these sensors, panel cleaning is timed based on data to improve panel safety and efficiency. With the soilingsensor, unnecessary cleaning of the panel surface is avoided and cost is reduced.
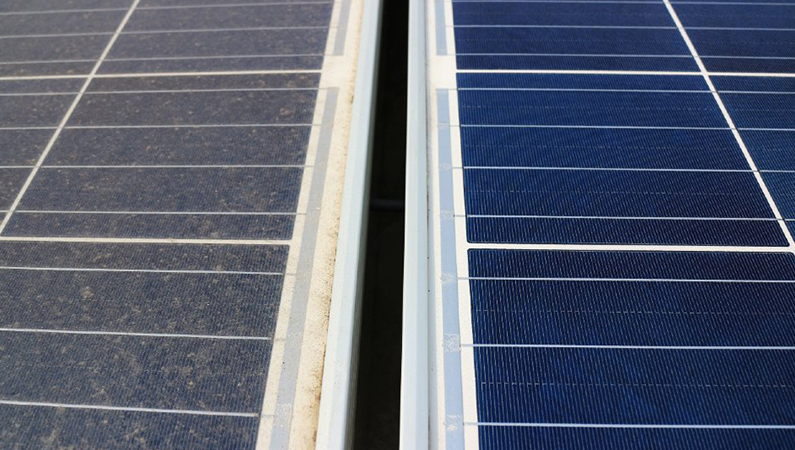

Differences Dusty and Clean Solar Panel
Fault Detection Process with SEVEN Sensor Data
Seven Sensor Solution devices bring together data from all sensors in the field. This data is usually integrated into the SCADA system. The sensors collect data in a centralized data collection unit where system performance is continuously monitored. Historical production and environmental conditions are compared with this collected data. Abnormal data, potential signs of malfunction or system deviations are analyzed, providing early warnings of potential failures or performance degradation. This allows maintenance teams to intervene quickly and effectively.
SEVEN Sensor Solution’s advanced sensor solutions make it possible to effectively manage fault detection, power generation continuity and preventive maintenance processes at SPP sites. Thanks to these sensors, system failures can be detected in advance, preventing costly losses and ensuring continuity in energy production.
You can review Seven Sensor Solution products for higher performance and fewer failures in your solar energy systems: “ https://www.sevensensor.com/products ”
