SEVEN offers the advantage of Daisy Chain connection, the easiest and best way to connect Modbus RTU – RS485 sensors, in all of its sensors. You can use the daisy chain connection in our products listed at the following link: “ https://www.sevensensor.com/products ”. So, what is the Daisy Chain connection that we frequently hear about and recommend as SEVEN? In this article, we will examine the Daisy Chain connection.
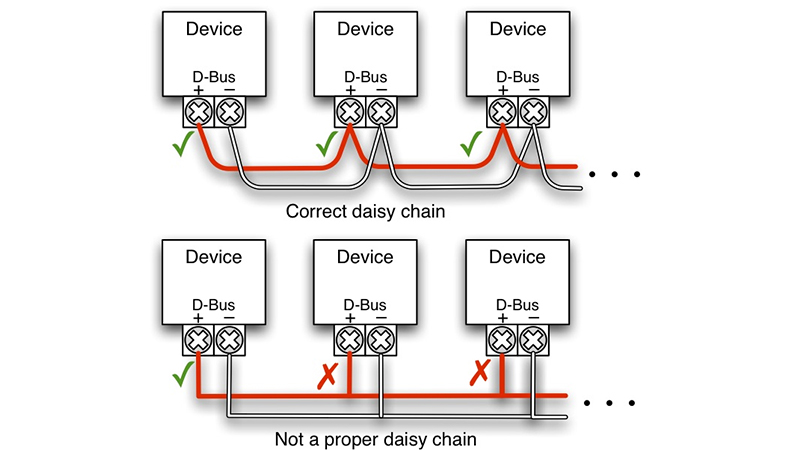
Daisy chain connection is a method of connecting many electronic devices or modules in series. In a daisy chain connection, each device both receives and transmits data; thus, communication continues until the device at the end of the chain. It has a 2-terminal connection port for communication via MODBUS. These terminals are mostly labeled as A [DATA +] and B [DATA -]. The wiring is done so that all these devices are connected in parallel. This means that all A terminals must be connected to each other, and all B terminals must be connected to each other. This connection method reduces cable clutter, makes it easier to expand the network, and is particularly suitable for sensor networks and data communication protocols.
How to Make a Daisy Chain Connection Between Sensors?
To establish a daisy chain connection between SEVEN sensors, the following steps are followed:
- Correct Sensor Selection
First of all, it should be known that SEVEN Sensor Solution sensors are capable of being connected in series and addressable. These features are sufficient for a daisy chain connection.
- Use of RS485 or Similar Serial Communication Protocol
In daisy chain connections, RS485 is generally preferred as the physical layer between sensors since it provides reliable data transmission over long distances and in noisy environments. All SEVEN products have Modbus RTU RS485 communication capability.
- Use of Termination Resistor
According to the diagram provided by SEVEN, 120-ohm termination resistors are placed at the first and last points of the network to prevent signal reflections on communication lines.
- Address Assignment
Each SEVEN Sensor Solution sensor can be assigned a unique address (between 1 and 247). This is usually done by the customer. In this way, a master device can query the correct sensor.
Note: Line topology is preferred. Star or ring topologies are not suitable for the daisy chain concept.
Important Considerations When Creating a Daisy Chain
- Cable Length: The total RS485 cable length should not exceed 1200 meters.
- Baud Rate: A lower baud rate is preferred over long distances (e.g., 9600 bps).
- Grounding and Protection: Proper grounding of the line and devices must be ensured. In SEVEN Sensor Solution products, sensors must be properly grounded using the black wire.

Sample Daisy Chain Connection Diagram Prepared by SEVEN Sensor Solution
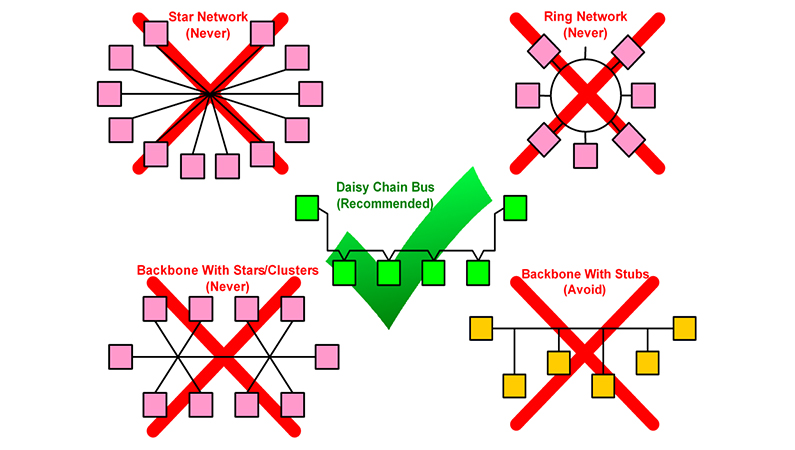
Not Recommended Topologies
Any other way of interconnecting devices is not recommended as it may cause communication problems or damage the entire system. Connection diagrams that are not recommended are included below.
Master/Slave Device Connection Not Recommended
- Star Network
All sensors are directly connected to one central node. This is how problems can arise:
- If the central point fails, the whole system crashes (single point of failure).
- It is particularly unsuitable for sensor systems spread over large areas.
- It creates difficulties in terms of time synchronization and data integrity.
- Cable length increases and communication problems may arise accordingly.
- Ring Network
The sensors are connected together in a ring. Problems can arise with this method as follows:
- If any connection breaks, the data in the whole ring is corrupted.
- Data delays are high; data has to travel around the entire ring.
- Error detection and repair is complex.
- Backbone with Stars/Clusters Network
It is a model where sub-star and cluster structures are connected to a network of communication lines. Problems can arise in this model as follows:
- Multiple central nodes are created and each of them is a potential point of failure.
- Again, the risk of “single point of failure” increases.
- Synchronization becomes difficult and network complexity increases.
- Backbone with Stubs
There are sensors connected to the main communication line via short branches. Problems can arise with this connection as follows:
- These short arms (stubs) cause signal reflections and noise.
- Load imbalance on the bus lines leads to data corruption over time.
- Poor fault tolerance and signal integrity problems.
So, daisy chain is the most accurate and reliable connection method. Daisy chain connection, especially when used with protocols such as Modbus RTU RS485, allows sensor networks to be established in an organized, reliable, and cost-effective manner. Good wiring, correct addressing, and proper termination directly affect the quality of this communication. In PV systems, the use of daisy chain connections for sensor wiring provides significant advantages.
SEVEN Sensor Solution can prepare all the sensors you need to be compatible with daisy chain connections and meet your requirements. You can contact SEVEN Sensor Solution via the following link: “ https://www.sevensensor.com/contact ”.