Measuring and monitoring efficiency in solar power plants is critical in terms of return on investment. In this context, Performance Ratio (PR) is one of the most commonly used indicators for evaluating the effectiveness of photovoltaic (PV) systems. In this article, we will discuss what PR is, common mistakes, improvement methods, and field applications at both technical and general levels.
What is PR in PV systems?
PR is the ratio of the actual energy production of a PV system to the theoretical maximum production. In other words, it shows how efficiently the system operates under the current weather conditions detected by sensors.
PR Calculation Formula:
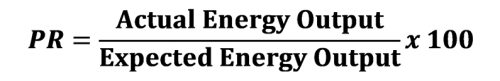
Not only the calculation of the PR (Performance Ratio) value, but also its correct interpretation plays a critical role in system performance analysis. Its unit is usually expressed as a percentage. PR values above 80% generally indicate that the photovoltaic (PV) plant is operating at the expected efficiency level, while values below this ratio may indicate the presence of problems such as malfunctions, contamination, shading, or inverter inefficiency that cause performance losses in the system. On the other hand, PR values exceeding 100% are typically due to data errors caused by measurement sensors being incompatible with PV system components and should be carefully addressed during the evaluation process.
What are the Important Points in PR Analysis?
1. Incorrect Irradiance Measurements
The irradiance data used in PR calculations is usually measured with a pyranometer or reference cell. Failure to calibrate sensors such as pyranometers or reference cells, not using high-quality sensors, or using them at incorrect angles can cause deviations in irradiance values and incorrect measurements.
2. Neglecting Temperature Compensation
PV module temperature is a critical parameter that directly affects panel efficiency. PV panels become less efficient with temperature. When the temperature effect is not taken into account, PR is calculated incorrectly.
3. Data Loss or Incomplete Measurements
Connection interruptions or software issues in data monitoring systems can lead to important data, such as energy production or irradiance, being recorded incompletely. Connection issues in recording systems or incorrect data collection directly negatively impact analysis results.
4. Neglecting AC/DC Conversion Losses
Inverter efficiency directly affects PR. However, some analyses do not take inverter losses into account. In this case, PR may appear high even though it is actually low. In other words, when inverter efficiency is not included, the PR value does not reflect reality.
5. Errors in Reference Area Calculations
The value of the PV area used in PR calculations is assumed to be constant. However, factors such as panel layout, shading effects, and panel type (monofacial/bifacial) can lead to incorrect area calculations. This results in an inaccurate PR value.
How to Increase PR Value
1. Correct Sensor Use
More accurate measurements can be made with high-quality pyranometers and module temperature sensors. For example, Class A thermopile pyranometers will provide more accurate results.
2. Periodic Maintenance and Calibration
Regular calibration of the sensors ensures the accuracy of the irradiance data. In addition, the Pyranometer and Irradiance sensor mount should be used in the same azimuth and Tilt angle as the panels with POA.
3. Albedo Measurements and Corrections in Bifacial Systems
For double-sided panels, albedo sensors must be used to account for light reflected from the ground.
4. Data Monitoring and Alarm Systems
Remote monitoring systems and warning mechanisms should be installed to detect instantaneous deviations.
Examples from Field Applications
1. Çorum/Merkez Palabıyık Village SPP Site:
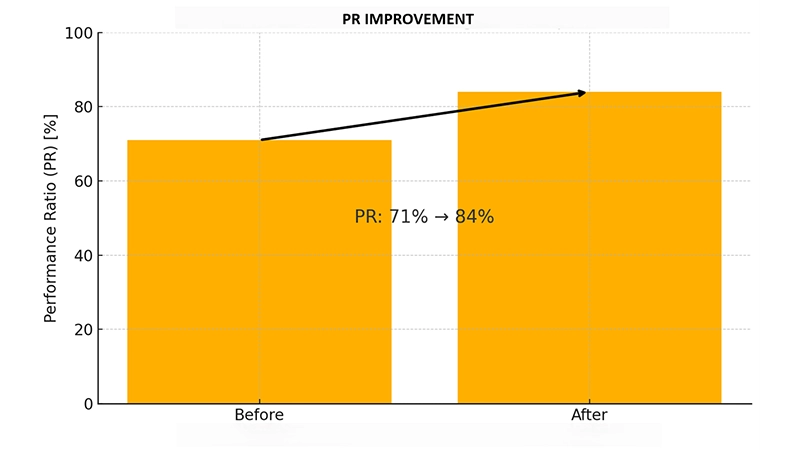
The PR value was determined to be 71% in the initial measurements. After the sensors were calibrated, the measurement accuracy increased and the PR value rose to 82%.
2. Çimko Sanko – Ayaş/Ankara SPP Site:
Due to inverter-related malfunctions, the AC output power remained low. After replacing the faulty inverters, the PR value increased from 76% to 84%.
3. Vim Energy -Panama SPP Site:
The albedo effect is ignored in the performance evaluation of the system. Accordingly, the current PR is high. When this albedo effect is included in the model, backward calculations show that the PR value should be 8% lower.
Performance Ratio (PR) analysis is one of the fundamental tools for efficiency control in solar energy projects. As seen in example field applications, the PR value can be optimized through proper sensor usage, regular maintenance, and appropriate data analysis. This shortens the investment payback period and increases system reliability.
For more technical information, please contact SEVEN Sensor Solution.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is PR (Performance Ratio)?
PR is the ratio of the actual production of the solar plant to the ideal production. It serves to measure efficiency.
2. What kind of problems are detected by PR analysis?
Problems that reduce efficiency such as panel pollution, inverter failure, shading can be identified.
3. How does PR analysis increase SPP efficiency?
Production losses can be prevented by recognizing low PR values early and intervening.