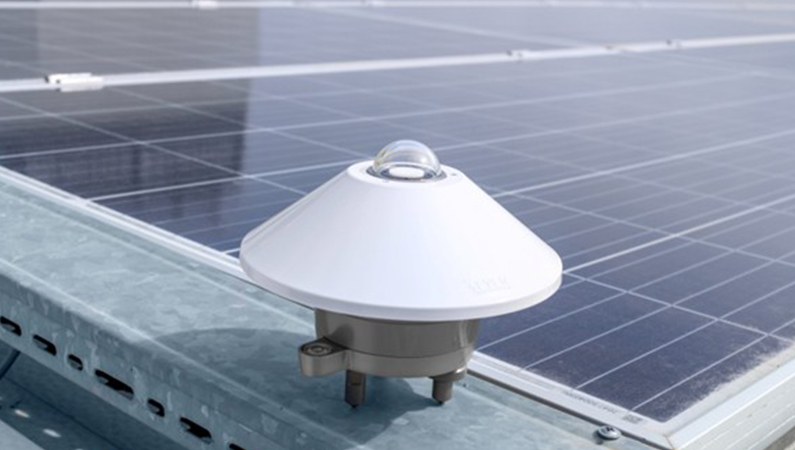
Pyranometers are critical for analyzing, monitoring, and optimizing the performance of solar energy systems. These devices measure global solar irradiance (GHI) from the sun, helping to accurately predict energy production, particularly in photovoltaic (PV) power plants. What are the classes of pyranometers according to ISO 9060 and IEC 61724-1 standards? In this article, we will examine the technical differences and selection criteria of Class A, B, and C pyranometers in detail.
What is a Thermopile Pyranometer?
A pyranometer is a sensor typically used in solar power plants to measure the total solar radiation (direct and diffuse) on a horizontal plane. The SEVEN Sensor Solution 3S-TP-MB-A Thermopile Pyranometer is an A Class sensor in accordance with ISO9060:2018 and IEC61724:2021. The 3S-TP-MB-A Thermopile Pyranometer is used in many fields, including solar power plants (SSP), meteorological stations, and academic researches.
What is the ISO 9060:2018 Standard?
ISO 9060:2018 is an international standard that defines the classification and technical requirements of solar radiation measurement equipment. This standard divides pyranometers into three main classes as follows:
- Class A (Precision Class): Formerly known as “Secondary Standard”, For example 3S-TP-MB-A
- Class B (Medium Class): Formerly known as “First Class”, For example 3S-TP-MB-B
- Class C (Basic Class): Formerly known as “Second Class”, For example 3S-TP-MB-C
Comparison of Pyranometer Classes According to ISO 9060:2018
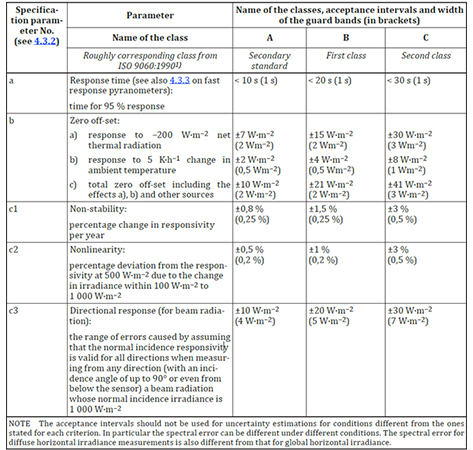
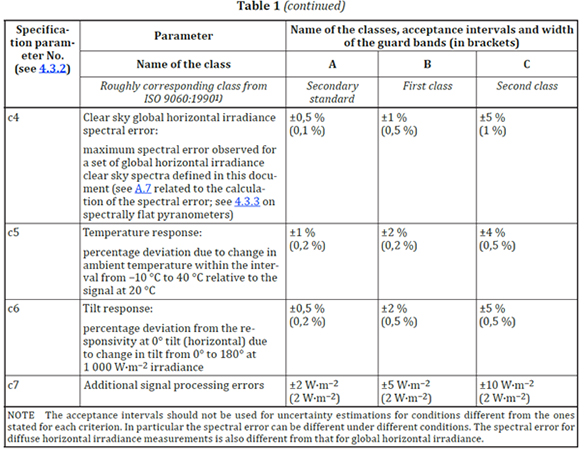
“Table 1 – Pyranometer Classification List” is found in the ISO9060:2018 standard. The table has been used directly without any changes.”
For technical explanations of the terms in the “name of the class” section above, please refer to our article “Technical Specifications of Pyranometers According to ISO 9060:2018 Standard.”
For the technical specifications and more of our Class A 3S-TP-MB-A Thermopile Pyranometer produced by SEVEN Sensor Solution in accordance with ISO 9060:2018, you can read the datasheet and user manual. Additionally, SEVEN Sensor Solution also offers Class B 3S-TP-MB-B and Class C 3S-TP-MB-C Thermopile Pyranometer models.
Compliance with IEC 61724-1 Standard
IEC 61724-1 regulates the devices and requirements used in performance monitoring systems for solar power plants. This standard determines the classes of pyranometers required based on the monitoring level of the plant:
Thanks to this compliance, investors and engineers can maximize system efficiency by selecting the right devices.
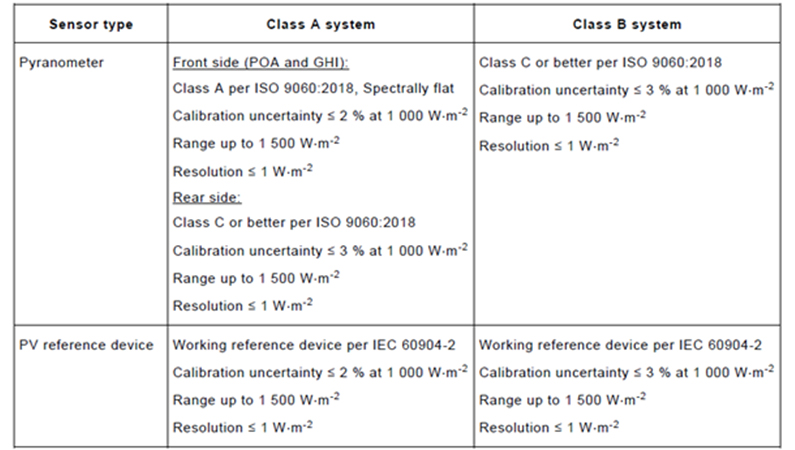
“Table 4 – Irradiance sensor requirements” is found in the IEC61724-1:2021 standard. The table has been used directly without any changes.”
Seven Sensor Soluton offers high accuracy SEVEN 3S-TP-MB-A Thermopile Pyranometer and all meteorological Sensor solutions in accordance with IEC 61724-1:2021 and ISO 9060:2018 standards.
What to Consider When Choosing a Pyranometer?
Pyranometers are classified according to performance criteria in accordance with the ISO 9060 standard:
- Class A (Secondary Standard): These are the most accurate pyranometers. They are used in research, calibration laboratories, or Class A monitoring systems in accordance with IEC 61724-1. Example Class A Pyranometer model SEVEN 3S-TP-MB-A.
- Class B (First Class): Offers medium accuracy. Suitable for commercial solar power plants and field monitoring applications. Example Class B Pyranometer model SEVEN 3S-TP-MB-B.
- Class C (Second Class): Developed for basic measurements. Preferred for education, general observation, or low-precision applications. Example Class C Pyranometer model SEVEN 3S-TP-MB-C.
When making a selection, the measurement accuracy required for your intended use, environmental conditions, and budget should be considered. Class A devices should be preferred for critical tasks such as performance monitoring, return on investment calculations, or fault detection.
Class A, B, and C pyranometers differ in terms of accuracy, response time, durability, and cost. The right choice determines data quality for both immediate performance and long-term production and financial analyses. Therefore, in addition to price, standard compliance and long-term data quality should also be considered when selecting a device.
SEVEN Sensor Solution, the first and only manufacturer of Thermopile Pyranometers in Turkey, produces sensors in compliance with ISO6090:2018 and IEC61724-1:2021 standards. For Thermopile Pyranometer solutions tailored to your site, please contact SEVEN Sensor Solution.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the classes of pyranometers and how are they determined according to the ISO 9060 standard?
The ISO 9060 standard divides pyranometers into three main classes according to performance criteria: Class A (Secondary Standard), Class B (First Class), and Class C (Second Class). This classification is based on measurement performance characteristics such as accuracy, linear response, directional response, temperature response, and stability. Devices with the highest sensitivity and accuracy are classified as Class A. Sample models suitable for pyranometer standards and classes; SEVEN 3S-TP-MB-A, SEVEN 3S-TP-MB-B, SEVEN 3S-TP-MB-C.
2. Which class of pyranometers does the IEC 61724-1 standard recommend for solar energy monitoring systems?
The IEC 61724-1 standard divides systems into Class A and B for monitoring the performance of photovoltaic (PV) systems. Class A systems typically use Class A pyranometers, while Class B systems are recommended to use at least Class B pyranometers.
3. How does the class of a pyranometer affect system performance?
The pyranometer class directly affects measurement accuracy. A higher class pyranometer provides more accurate and reliable measurements.
